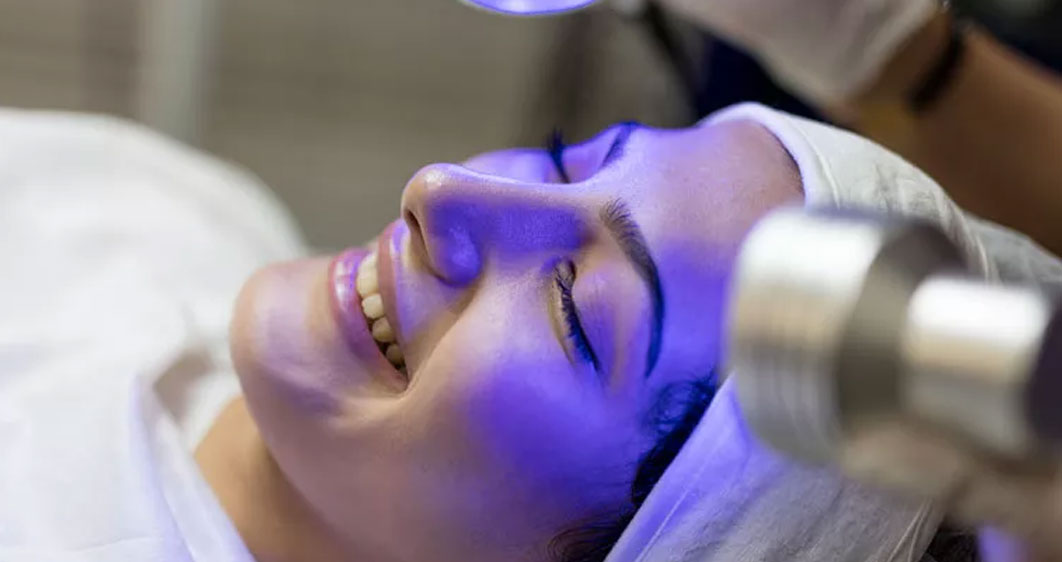
Blue Light Therapy Treatment
Blue light therapy treatment is a non-invasive treatment that has gained immense popularity in recent years, particularly for treating skin conditions such as acne, inflammation, and sun damage. It utilizes specific wavelengths of blue light to target and improve various dermatological concerns. Dermatologists and skincare specialists often recommend blue light therapy for individuals who seek an alternative to traditional treatments like creams or medications, due to its effectiveness and minimal side effects.
In this content, we’ll explore the mechanism, benefits, and uses of blue light therapy for skin treatment, along with its potential risks and how it compares to other therapies.
What is Blue Light Therapy?
Blue light therapy involves the use of blue light, typically in the range of 405 to 420 nanometers, to penetrate the skin and treat underlying skin issues. The light is absorbed by the skin and works primarily by targeting bacteria and inflammation that contribute to skin problems.
Blue light therapy is often used in dermatological practices, but home devices are also available for those who want to incorporate this blue light therapy treatment into their skincare routine. It’s a painless procedure and doesn’t require the use of chemicals or medications, making it a preferred choice for people who are looking for natural blue light therapy treatment methods.
How Does Blue Light Therapy Work for Skin?
Blue light therapy works by targeting the porphyrins in bacteria. Porphyrins are compounds found in Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), the bacteria responsible for causing acne. When blue light is applied to the skin, it activates the porphyrins, creating a toxic environment for the bacteria and ultimately destroying it.
This mechanism of action is particularly effective in treating mild to moderate acne. Additionally, blue light has anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce swelling, redness, and irritation, all of which are common symptoms of acne.
Blue light therapy is also believed to stimulate collagen production, though this effect is more prominently seen with red light therapy, which is sometimes combined with blue light for comprehensive skin rejuvenation.
Uses of Blue Light Therapy for Skin
Blue light therapy has proven to be versatile, with applications for treating various skin conditions. Here are some of the most common uses:
1. Acne Treatment
One of the primary uses of blue light therapy is in the treatment of acne. Blue light can effectively reduce both inflammatory and non-inflammatory acne lesions by killing the acne-causing bacteria (P. acnes) and reducing inflammation in the skin. It’s often recommended for individuals who experience moderate breakouts or those who cannot tolerate conventional acne medications, such as topical retinoids or oral antibiotics.
Many patients notice an improvement in their skin after just a few sessions of blue light therapy. It’s especially effective when combined with salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide treatments, as these ingredients help to unclog pores while the blue light kills bacteria.
2. Sun Damage and Premature Aging
Blue light therapy is also used to treat sun damage and photoaging, including pigmentation, fine lines, and rough texture caused by excessive UV exposure. Blue light works by removing damaged skin cells and promoting cellular turnover, which helps rejuvenate the skin and improve overall skin tone.
Though blue light therapy alone can help treat sun damage, it’s often combined with red light therapy for enhanced anti-aging benefits. Red light therapy penetrates deeper into the skin, promoting collagen production and improving elasticity, while blue light targets the surface-level concerns.
3. Actinic Keratosis (Precancerous Skin Lesions)
Blue light therapy, in combination with a photosensitizing agent, is FDA-approved for the treatment of actinic keratosis, a precancerous skin condition caused by long-term exposure to the sun. Actinic keratosis appears as rough, scaly patches on the skin, and if left untreated, can develop into skin cancer.
In this blue light therapy treatment, known as photodynamic therapy (PDT), a photosensitizing cream is applied to the affected area, which is then exposed to blue light. The light activates the cream, selectively destroying the precancerous cells without harming the surrounding healthy tissue. This makes blue light therapy an effective, non-invasive treatment for actinic keratosis.
4. Rosacea and Other Inflammatory Skin Conditions
Blue light therapy’s anti-inflammatory effects make it an effective treatment for rosacea and other inflammatory skin conditions. Rosacea causes redness, flushing, and visible blood vessels on the face, and can be challenging to manage with traditional treatments.
By calming inflammation and reducing the number of bacteria on the skin, blue light therapy can help minimize rosacea flare-ups and improve skin appearance. However, it’s essential to consult a dermatologist before using blue light therapy for rosacea, as the condition can vary in severity.
Benefits of Blue Light Therapy for Skin
Blue light therapy offers several advantages for skin health, making it a popular treatment option:
Non-Invasive: Blue light therapy does not involve any surgical procedures or chemical treatments, reducing the risk of scarring or irritation.
Painless: The procedure is painless and comfortable, with most patients reporting no discomfort during treatment.
Minimal Side Effects: Compared to other treatments like oral antibiotics or chemical peels, blue light therapy has minimal side effects, making it suitable for sensitive skin.
No Downtime: There is no recovery period required, and patients can resume their regular activities immediately after a session.
Versatile: It can be used to treat a variety of skin conditions, including acne, sun damage, actinic keratosis, and more.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While blue light therapy is generally safe, some potential side effects may occur, especially if not administered correctly. Common side effects include:
Redness and Irritation: Some patients may experience mild redness or irritation after a session, though this typically subsides within a few hours.
Dryness: Blue light can dry out the skin, especially in individuals with sensitive skin. Using a gentle moisturizer can help alleviate this.
Photosensitivity: Blue light therapy can increase skin sensitivity to sunlight. It’s essential to wear sunscreen and limit sun exposure after treatment to prevent sunburn or further damage.
In-Clinic vs. At-Home Blue Light Therapy
Blue light therapy is available both in clinical settings and through at-home devices. In-clinic treatments typically involve more potent blue light and may yield faster results. They are administered under professional supervision, ensuring safety and efficacy.
At-home devices, while convenient, generally use lower intensities of blue light and may take longer to produce noticeable improvements. They are, however, a good option for maintaining results between professional treatments.
Conclusion
Blue light therapy is a highly effective, non-invasive treatment option for various skin conditions, particularly acne, sun damage, and actinic keratosis. Its ability to target bacteria, reduce inflammation, and promote skin healing makes it a valuable addition to skincare routines. With minimal side effects and no downtime, blue light therapy offers a safe and convenient way to achieve clearer, healthier skin. However, as with any treatment, consulting a dermatologist to determine its suitability for your skin type and condition is recommended.